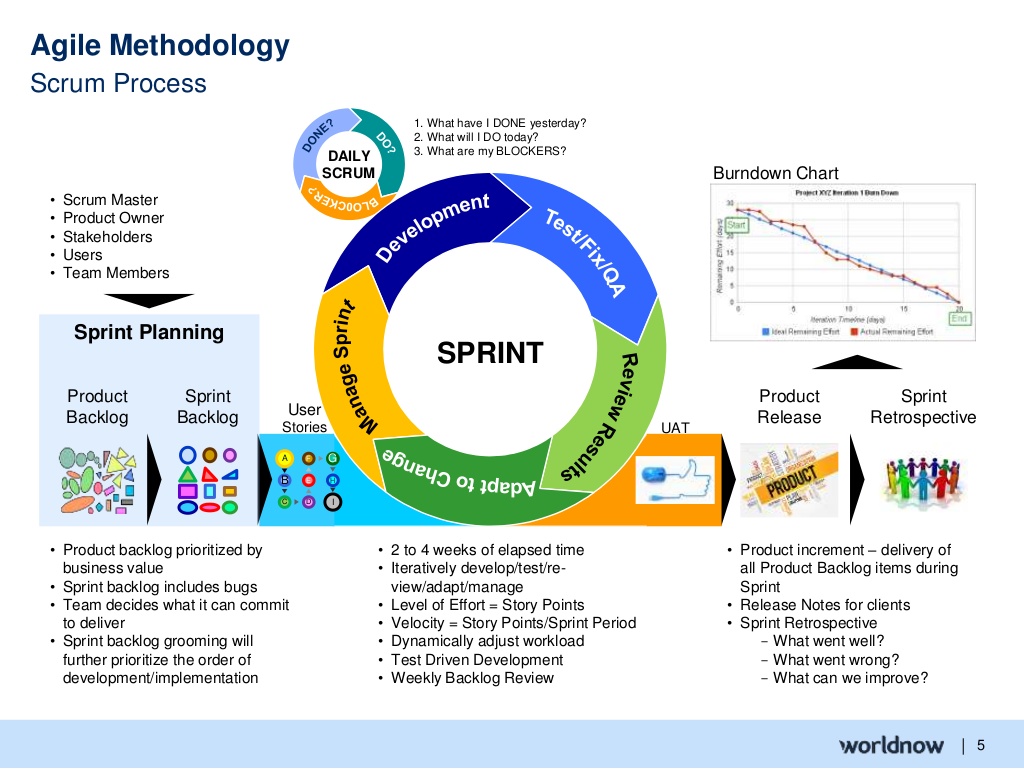
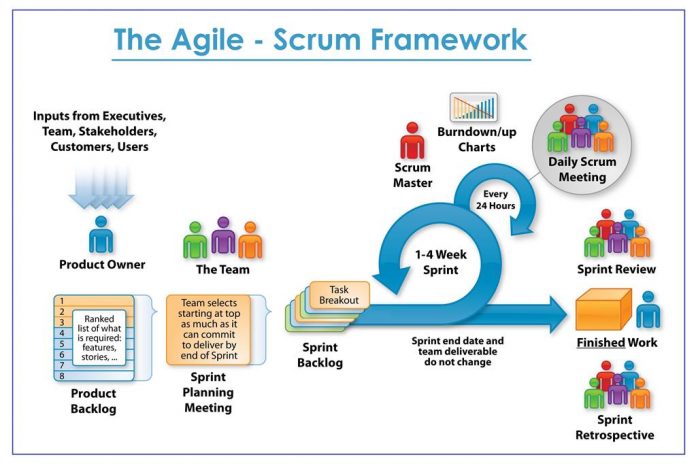
Scrum is one of the most popular Agile frameworks originally used for developing software projects. Scrum is characterized by fixed time iterations called sprints which usually last 2-4 weeks. At the end of the sprint, all team members discuss further planning.
Scrum includes the roles, responsibilities and meetings which are never changed. For example, Scrum follows 4 obligatory components that are considered as a sprint structure: sprint planning, daily Scrum meeting (15 minutes), sprint review and retrospective. During the sprint, the team uses visual methods to show the process of the work and receive customer’s feedback.
There are 3 roles in Scrum:
- Product owner is familiar with business requirements (product type), knows the goal he wants to accomplish and brings the view of his idea. Product owner is focused on business as well as market requirements paying attention to the overall backlog. He defines the timeline, gives instructions and collaborates with the team and other stakeholders to ensure that everybody understands the product elements. Product owner is not a project manager. He is responsible for determining goal and vision.
- Scrum master is a coach of the team and helps to do his best to accomplish the goal. It implies facilitating daily meetings, considering requirements and obstacles, working with the product owner to ensure the product is ready for the sprint. Besides, scrum master is responsible for making the team fulfil the scrum principles. Scrum master has no authority over scrum team, but he has authority over scrum process. For example, scrum master can’t make any team member perform the task, but he can suggest the task for the sprint.
- Scrum team consists of 5-7 team members. Every team member works on the project together and helps each other. In contrast with traditional development approaches, there’re no common functions such as developer, designer or QA engineer. Everybody gets involved in the project and teams up. Scrum team has the plan for each sprint where a number of tasks are defined.
Moreover, scrum has a set of features that makes the approach distinguished:
- Product backlog: product owner and scrum team prioritize the tasks (it’s based on user stories and requirements). Product description is not considered as a task, but it is included in the obligatory list of functions. Then scrum team manages priorities for each sprint.
- Sprint planning: before holding the sprint, product owner defines the tasks which are to be discussed at sprint planning event. Then scrum team sorts out tasks for every sprint. So the tasks are transferred from product backlog to sprint backlog.
- Backlog refinement/grooming: at the end of each sprint, scrum team and product owner meet to ensure that everything is ready to complete the next sprint. Team can remove some user stories which are not related to the main task, create new user stories, reprioritize tasks and divide tasks into subtasks. The key goal is to define relevant tasks which serve the purpose.
- Daily scrum meetings: it is held every morning and lasts about 15 minutes where every scrum team member discusses his plans and issues he has faced when completing the sprint. The meeting helps everybody keep informed.
- Sprint review meeting: it’s held at the end of every sprint where every team member presents the task he has accomplished by the time. Usually, it’s forbidden to use PowerPoint slides.
- Sprint retrospective meeting: at the end of every sprint, the team defined how good scrum is and discusses the changes which are to be implemented for next sprint. Besides, the team discusses the positive experience and negative experience and what could happen if did it differently.
There are some tools used in scrum:
- Scrum board can be divided into following columns: to do, work in progress, and done. The board is kept updated during the sprint. For example, if there’s a new task appeared, it is written on the card and put on the board.
- User stories describe software from user’s point of view. It includes the type of the user, what and why he wants it. The short stories have their own structure: as a <user type>, I want to <complete a task> in order to <accomplish the goal>.
- Burndown chart represents all outstanding work. It helps to warn the team if something goes wrong and show the impact of the decisions made by the team.
- Timeboxing is a specified time period during which the team works toward a common goal.
- Icebox is a place where user stories which are recorded but not developed are kept.
Read also: System Development Life Cycle. Magento Certification, Agile Methodology. Magento Certification.