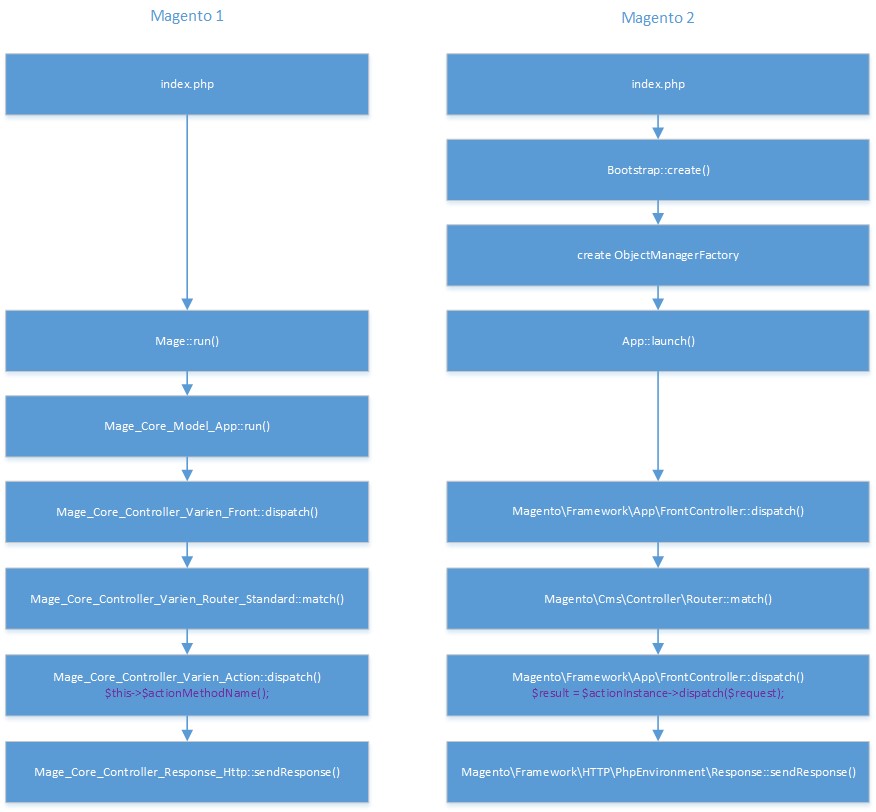
If you’re good at Magento 1, you will be able to find substantial similarities between Magento 1 and Magento 2. First off, let’s look at the pictures showing us the paths of both Magento versions.
Request flow in Magento 1.x
Magento 1.x routes all requests through index.php file which is placed in the Magento base directory. At the end of the file,
|
1 |
Mage::run($mageRunCode, $mageRunType); |
is called.
App
app\Mage.php
Mage:: run($code = ”, $type = ‘store’, $options = array())
Mage::run() makes the basic run time environment be set up while the request be processed. That process is started by delegating to Mage_Core_Model_App::run().
|
1 |
self::$_app = new Mage_Core_Model_App(); |
Frontend main entry point
app\code\core\Mage\Core\Model\App.php
|
1 |
Mage_Core_Model_App::run($params) |
Load base system configuration (local.xml and config.xml files) from app/etc/modules/*.xml.
Base configuration provides an ability to initialize DB connection and cache backend
|
1 |
$this->baseInit($options); |
Initialize active modules configuration and data
|
1 |
$this->_initModules(); |
Initialize the store currently running
|
1 |
$this->_initCurrentStore($scopeCode, $scopeType); |
Load the request information into the model
|
1 |
$this->_initRequest(); |
Update/create versions of modules in core_resource whenever needed.
|
1 |
\Mage_Core_Model_Resource_Setup::applyAllDataUpdates() |
Dispatch controller
|
1 |
$this->getFrontController()->dispatch(); |
Routing
app\code\core\Mage\Core\Controller\Varien\Front.php
Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Front::dispatch()
Check if there’s url rewrite as well as redirect to url
|
1 |
$this->_getRequestRewriteController()->rewrite(); |
Routers check the request URL to match patterns
|
1 2 3 |
if ($router->match($request)) { break; } |
If a controller and action are matched, the controller file will be included, instantiated and action method will be called.
– Process Admin scope Requests
File: app/code/core/Mage/Core/Controller/Varien/Router/Admin.php
Class: Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Router_Admin
– Process Front end scope Requests
File: app/code/core/Mage/Core/Controller/Varien/Router/Standard.php
Class: Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Router_Standard
– Custom.
– Default. Process no-route action, 404 page.
File: app/code/core/Mage/Core/Controller/Varien/Router/Default.php
Class: Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Router_Default
The further process will be considered using a frontend controller as an example: app/code/core/Mage/Core/Controller/Varien/Router/Standard.php
Class: Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Router_Standard::match()
The “match” method sets values to module name, controller and action. Then dispatch action
|
1 |
$controllerInstance->dispatch($action); |
app/code/core/Mage/Core/Controller/Varien/Action.php
Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Action::dispatch($action)
– Frontend Controller
File: app\code\core\Mage\Core\Controller\Varien\Action.php
Class: Mage_Core_Controller_Front_Action::dispatch($action)
– Admin Controller
File: app\code\core\Mage\Adminhtml\Controller\Action.php
Class: Mage_Adminhtml_Controller_Action::dispatch($action)
Call action. Action method will instantiate and call methods on models, depending on the request
|
1 |
$this->$actionMethodName(); |
For the main page the following method will be called: Mage_Cms_IndexController::indexAction().
Rendering
Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Action::loadLayout ($handles = null, $generateBlocks = true, $generateXml = true)
Mage_Core_Controller_Varien_Action::renderLayout($output=”)
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
class My_Test_IndexController extends Mage_Core_Controller_Front_Action { public function indexAction() { $this->loadLayout (); $this->renderLayout (); } } |
Flushing Output
Mage_Core_Controller_Response_Http::sendResponse()
Request Flow in Magento 2.x
Similar to Magento 1, Magento 2 routes requests through index.php.
Bootstrap
index.php
$bootstrap = \Magento\Framework\App\Bootstrap::create(BP, $_SERVER);
This method creates the instance of object manager factory
\vendor\magento\framework\App\Bootstrap.php
Magento\Framework\App\Bootstrap::create()
index.php
Factory method to create application instances
|
1 |
$app = $bootstrap->createApplication('Magento\Framework\App\Http'); |
index.php
Runs an application
|
1 |
$bootstrap->run($app); |
App
Magento\Framework\App\Bootstrap::(AppInterface $application)
|
1 |
$response = $application->launch(); |
Magento\Framework\App\Http::launch()
When launching the app, first we determine and specify area code
|
1 2 |
$areaCode = $this->_areaList->getCodeByFrontName($this->_request->getFrontName()); $this->_state->setAreaCode($areaCode); |
Then configure object manager for definite area
|
1 |
$this->_objectManager->configure($this->_configLoader->load($areaCode)); |
As we can see, area isolation is better in Magento 2.
Routing
Init & dispatch controller
|
1 2 |
$frontController = $this->_objectManager->get('Magento\Framework\App\FrontControllerInterface'); $result = $frontController->dispatch($this->_request); |
Perform action and generate response
Magento\Framework\App\FrontController::dispatch(RequestInterface $request)
Here we can see that when router finds matches, action class (\Magento\Framework\App\ActionFactory) instance gets back. After that, front controller will call dispatch method on action class instance.
Validate and Match Cms Page and modify request
|
1 |
$actionInstance = $router->match($request); |
Magento\Cms\Controller\Router::match(\Magento\Framework\App\RequestInterface $request)
Dispatch request
Magento\Framework\App\FrontController::dispatch(RequestInterface $request)
|
1 |
$result = $actionInstance->execute(); |
For the main page, the following method will be called:
Magento\Cms\Controller\Index\Index\Interceptor::execute()
Rendering
View::loadLayout()
View::renderLayout()
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Class Index extends \Magento\Framework\App\Action\Action { public function execute() { $this->_view->loadLayout(); $this->_view->getLayout()->iniMessages(); $this->_view->renderLayout(); } } |
Flushing Output
Magento\Framework\HTTP\PhpEnvironment\Response::sendResponse()