Backend Model performs the loading, saving, deleting, validation of the attribute value. Source Model provides a list of attribute values, which is used for the dropdown/multiselect attributes. Frontend Model performs attribute mapping on the frontend.
Here is a list of questions that we will consider in this article:
How would you add dropdown/multiselect attributes?
What other possibilities do you have when adding an attribute (to a product, for example)?
Describe how to implement the interface for attribute frontend models. What is the purpose of this interface? How can you render your attribute value on the frontend? Identify the purpose and describe how to implement the interface for attribute source models.
For a given dropdown/multiselect attribute, how can you specify and manipulate its list of options?
Identify the purpose and describe how to implement the interface for attribute backend models. How (and why) would you create a backend model for anattribute?
Describe how to create and customize attributes. How would you add a new attribute to the product, category, or customer entities? What is the difference between adding a new attribute and modifying an existing one?
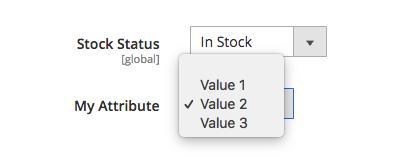
How to add dropdown/multiselect attributes
You can create attributes through the setup script (Vendor\Module\Setup\InstallData or Vendor\Module\Setup\UpgradeData) or in the admin panel (for products only). In order to create the dropdown/multiselect attributes, you must specify the frontend_input attribute as “select” or “multiselect” for a single or multiple choice respectively. Additionally, you must specify the source model, which will point to a list of possible values. If the source model is Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Source\Table, then in the ‘’option’’ property when creating an attribute through the setup script, you can specify the possible values of this attribute.
Here is an example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
<?php namespace Vendor\Module\Setup; use Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetupFactory; use Magento\Framework\Setup\InstallDataInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface; class InstallData implements InstallDataInterface { /** * @var EavSetupFactory */ protected $eavSetupFactory; public function __construct(EavSetupFactory $eavSetupFactory) { $this->eavSetupFactory = $eavSetupFactory; } public function install(ModuleDataSetupInterface $setup, ModuleContextInterface $context) { $eavSetup = $this->eavSetupFactory->create(['setup' => $setup]); $eavSetup->addAttribute( \Magento\Catalog\Model\Product::ENTITY, 'my_attribute', [ 'type' => 'int', 'label' => 'My Attribute', 'input' => 'select', 'source' => \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Source\Table::class, 'required' => false, 'option' => ['values' => ['Value 1', 'Value 2', 'Value 3']] ] ); } } |
Other possibilities for adding an attribute (to a product, for example)
The EAV attribute contains several properties that we can specify.
The Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Setup\PropertyMapper class contains the conversion of property names in the setup script to the names of the EAV attribute properties in the database.
|
Setup script property |
Database property |
Default property |
| attribute_model | attribute_model | null |
| backend | backend_model | null |
| type | backend_type | varchar |
| table | backend_table | null |
| frontend | frontend_model | null |
| input | frontend_input | text |
| label | frontend_label | null |
| frontend_class | frontend_class | null |
| source | source_model | null |
| required | is_required | 1 |
| user_defined | is_user_defined | 0 |
| default | default_value | null |
| unique | is_unique | 0 |
| note | note | null |
| global | is_global | \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\ScopedAttributeInterface::SCOPE_GLOBAL |

Magento Development Services
Take your online store to the next level with BelVG Magento development
Visit the storeYou can also specify:
- sort_order — attribute position, recorded in eav_entity_attribute;
- group — adds an attribute to a specific group;
- option — a list of values for the dropdown/multiselect attributes.
Additionally, Magento/Catalog contains the following properties (according to \Magento\Catalog\Model\ResourceModel\Setup\PropertyMapper):
|
Setup script property |
Database property | Default property |
| input_renderer | frontend_input_renderer | null |
| global | is_global | \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\ScopedAttributeInterface::SCOPE_GLOBAL |
| visible | is_visible | 1 |
| searchable | is_searchable | 0 |
| filterable | is_filterable | 0 |
| comparable | is_comparable | 0 |
| visible_on_front | is_visible_on_front | 0 |
| wysiwyg_enabled | is_wysiwyg_enabled | 0 |
| is_html_allowed_on_front | is_html_allowed_on_front | 0 |
| visible_in_advanced_search | is_visible_in_advanced_search | 0 |
| filterable_in_search | is_filterable_in_search | 0 |
| used_in_product_listing | used_in_product_listing | 0 |
| used_for_sort_by | used_for_sort_by | 0 |
| apply_to | apply_to | null |
| position | position | null |
| used_for_promo_rules | is_used_for_promo_rules | 0 |
| is_used_in_grid | is_used_in_grid | 0 |
| is_visible_in_grid | is_visible_in_grid | 0 |
| is_filterable_in_grid | is_filterable_in_grid |
0 |
How to implement the interface for attribute frontend models and the purpose of this interface. How to render attribute value on the frontend
To create a Frontend model, you need to create a class that is inherited from Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Frontend\AbstractFrontend and to override the getValue method.
Then you need to specify the frontend_model of the attribute as the name of the created class.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
class TestFrontend extends \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Frontend\AbstractFrontend { public function getValue(\Magento\Framework\DataObject $object) { $attribute_code = $this->getAttribute()->getAttributeCode(); $value = $object->getData($attribute_code); return nl2br(htmlspecialchars($value)); } } |
The purpose of the interface is to reduce the dependence of the code (dependency inversion principle).
Identify the purpose and describe how to implement the interface for attribute source models
The model is used to provide a list of attribute values for the dropdown/multiselect attributes. Here is an example of the source model implementation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
class TestSource extends \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Source\AbstractSource { public function getAllOptions() { if (!$this->_options) { $this->_options = [ ['label' => __('Label 1'), 'value' => 'value 1'], ['label' => __('Label 2'), 'value' => 'value 2'], ['label' => __('Label 3'), 'value' => 'value 3'], ['label' => __('Label 4'), 'value' => 'value 4'] ]; } return $this->_options; } } |
How to specify and manipulate the list of options for a given dropdown/multiselect attribute
If the source model is the Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Source\Table class or it is inherited from it, then the values are stored in the eav_attribute_option_value table. You can add them when creating an attribute in the option property, or call the Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetup->addAttributeOption($option) method.
If the source model is not inherited from Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Source\Table, then in order to change the list of values you can:
- create a plugin on the getAllOptions method in the source model;
- create a new source model that is inherited from the modified class, change the behavior of the getAllOptions method and specify a new source model in the attributes.
How to implement the interface for attribute backend models. How to create a backend model for an attribute
The purpose of creating a backend model is to change the loading/saving/deleting/validating the attribute value.
Here is an example of validating an attribute value:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
class TestBackend extends \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Backend\AbstractBackend { public function validate($object) { $attribute_code = $this->getAttribute()->getAttributeCode(); $value = $object->getData($attribute_code); if ($value == 'test') { throw new \Magento\Framework\Exception\LocalizedException(__("Value can't be test")); } return true; } } |
How to create and customize attributes. How to add a new attribute to the product, category, or customer entities. The difference between adding a new attribute and modifying an existing one
Vendor\Module\Setup\InstallData and Vendor\Module\Setup\UpgradeData setup scripts are used for creating/modifying an attribute.
Attributes for products can also be created through the admin panel.
To add an attribute, use the Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetup->addAttribute($entityTypeId, $code, $attr) method, to change and attribute, use the Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetup->updateAttribute($entityTypeId, $id, $field, $value = null, $sortOrder = null) method. However, if the addAttribute method is called and the attribute already exists, the updateAttribute method will be called automatically. Thus, there is no particular difference between adding a new attribute and changing an existing one, if you use the addAttribute method.
That is what managing attributes in Magento 2 looks like, thank you for reading. You can learn more about EAV model on our blog in the EAV in Magento 2 article.
Looking for an experienced Magento 2 development team? Turn to BelVG!